AWS Systems Manager (SSM) Node Executor Plugins
AWS Systems Manager (SSM) Node Executor Plugins
Available in PagerDuty Process Automation Commercial products.
Overview
The Node Executor and File Copier plugins use AWS Systems Manager to send commands, files and scripts to remote nodes.
Using the SSM plugins allows for Process Automation to communicate with EC2 instances through the SSM service, rather than another communication protocol - such as SSH. Process Automation sends commands to the Systems Manager service, and then the Systems Manager agents pull their tasks onto their host EC2s. In addition, S3 is used to pass scripts and files to remote nodes.

Configuration and Credential Settings
There are three components of the setup for using SSM with Process Automation:
- SSM and IAM setup on the remote EC2 nodes.
- IAM permissions for Process Automation.
- S3 Bucket setup. Required for executing scripts and sending files to EC2s, but not required for sending individual commands.
SSM Setup on Remote EC2 Nodes
- Ensure the SSM Agent is running on remote EC2 instances. This can be done following this AWS documentation.
- Associate an IAM role with the remote EC2 instances that allows for the SSM agent to retrieve tasks from the SSM service.
- AWS provides a prebuilt policy: AmazonSSMManagedInstanceCore that provides the necessary permissions for this operation.
Heads Up!
In order to send scripts and files to EC2 instances, the SSM agents also need to be able to retrieve objects from S3. Be sure to add the
s3:GetObjectands3:ListObjectpermissions to the remote EC2s IAM role as well.{ "Version": "2012-10-17", "Statement": [ { "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "s3:GetObject", "s3:ListBucket" ], "Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::<<YOUR S3 BUCKET>>/*" } ] } - Add the instances to the SSM inventory. This can be done using the Quick Setup Host Management.
- You can test that you have configured Systems Manager correctly by manually using the Run Command feature from AWS:
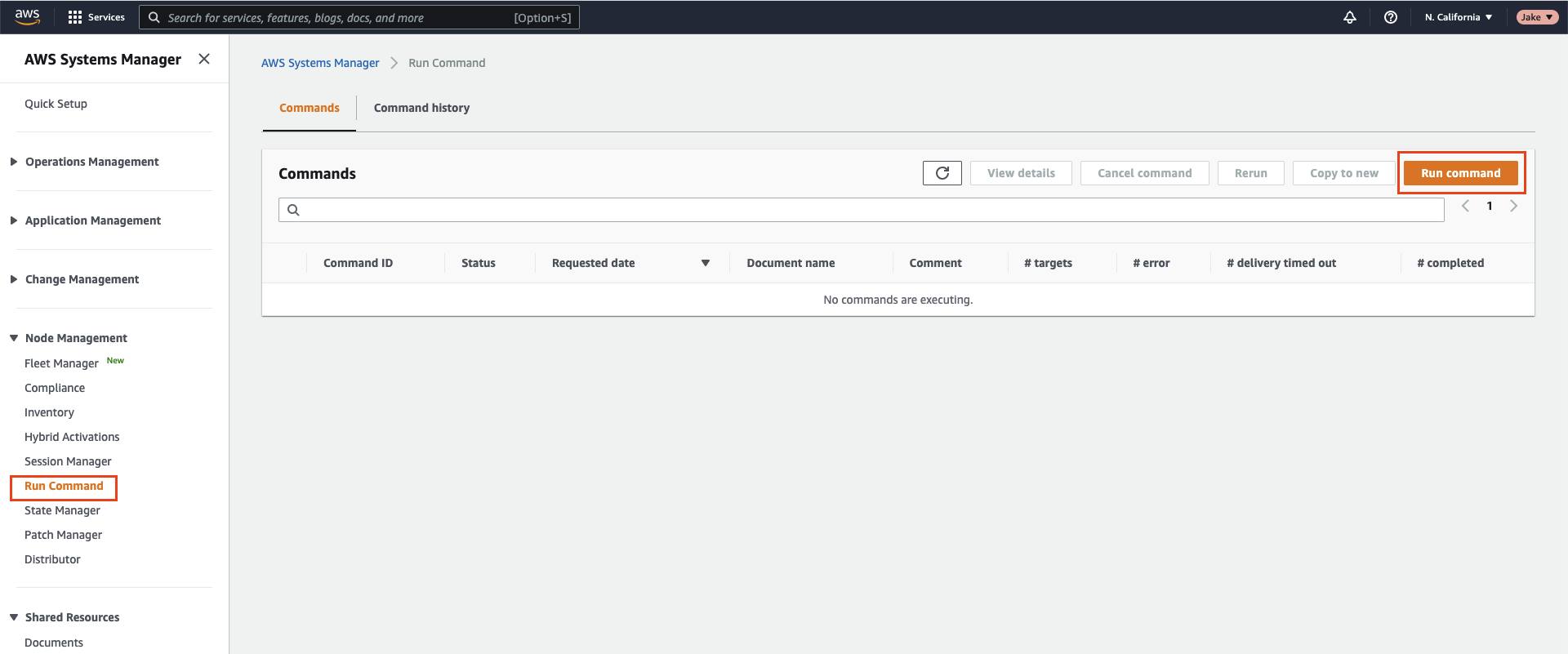
- Use the
AWS-RunShellScriptorAWS-RunPowerShellScript(for Windows) to test that SSM has been set up properly for the remote EC2 nodes.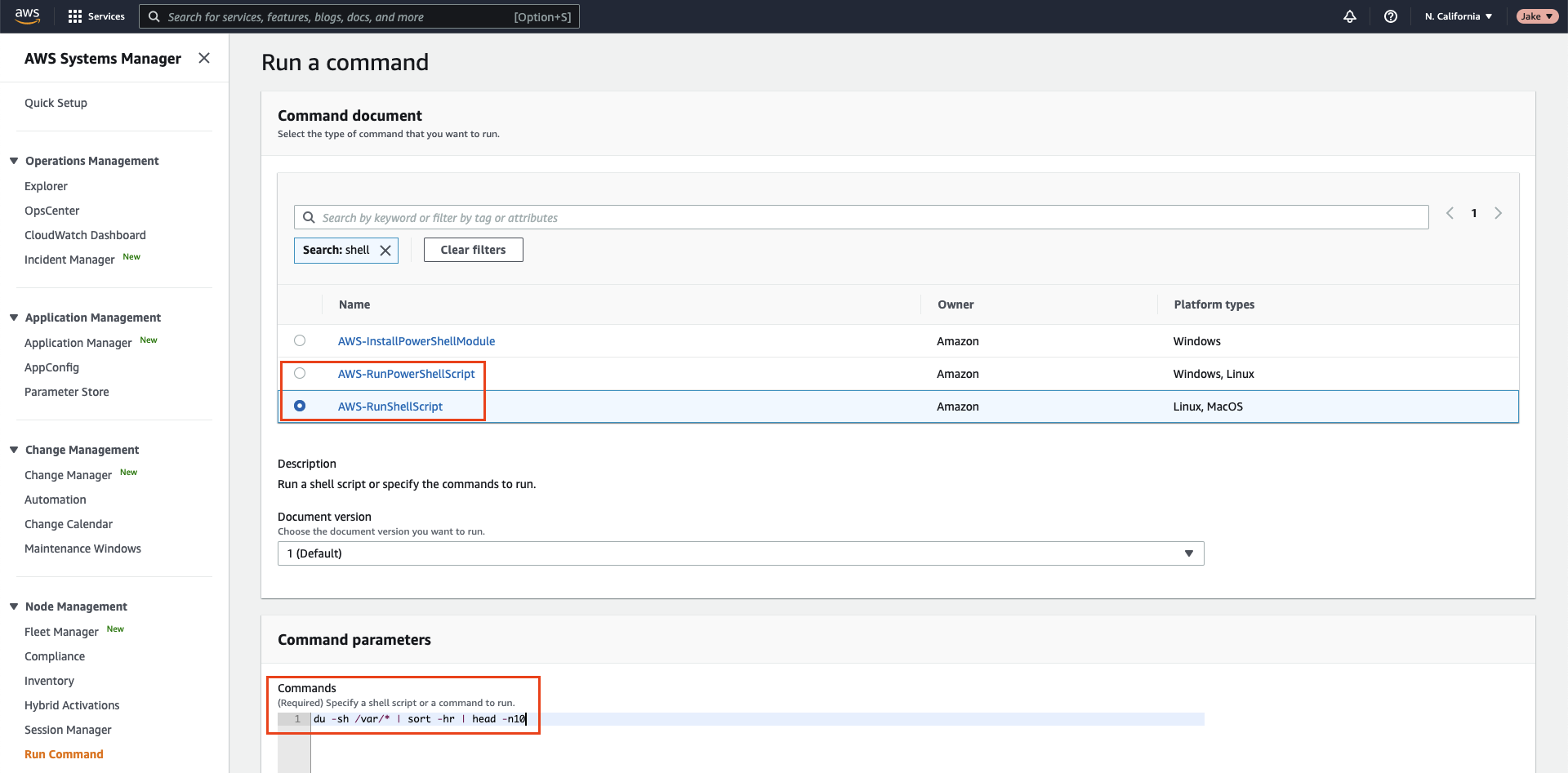
- Use the
Additional documentation on this setup can be found in the Setting up AWS Systems Manager for EC2 instances.
IAM Permissions Setup for Process Automation
In order for Process Automation to communicate with remote EC2 instances using SSM, it needs to have permissions to send commands to the SSM service. Amazon provides a prebuilt IAM Policy, AmazonSSMAutomationRole that can be used for providing the SSM permissions to Process Automation's IAM Role. However, it is recommended to only use this role for testing as it has fairly broad permissions.
Here are steps to use a more secure permissions set:
- Create a new IAM Policy with the following permissions:
Heads Up!
Be sure to replace
<<your AWS account ID>>with the Account ID where the remote EC2 instances reside.{ "Version": "2012-10-17", "Statement": [ { "Sid": "VisualEditor0", "Effect": "Allow", "Action": "ssm:SendCommand", "Resource": [ "arn:aws:s3:::*", "arn:aws:ssm:*::document/AWS-RunShellScript", "arn:aws:ssm:*::document/AWS-RunPowerShellScript", "arn:aws:ssm:*::document/AWS-RunRemoteScript", "arn:aws:ec2:*:<<your AWS account ID>>:instance/*" ] }, { "Sid": "VisualEditor1", "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "ssm:ListCommands", "ssm:ListCommandInvocations", "ssm:GetCommandInvocation", "logs:GetLogEvents" ], "Resource": "*" } ] } - Attach this policy with the IAM Role that is associated with Process Automation. If Process Automation is hosted on EC2, then follow these steps to modify the IAM Role of an EC2. If hosted on ECS, then follow these steps.
IAM Role for ECS
If running Process Automation on ECS, then this IAM Policy needs to be attached to the Task Role, not the Task Execution Role.
S3 Bucket Permissions
In order for scripts and files to be picked up by the SSM agents on the remote nodes, the files are (temporarily) passed through an S3 bucket.
- Create an S3 bucket that has a bucket policy that allows for objects to be uploaded to it by the IAM policy associated with Process Automation.
- Include a permission statement in this policy that allows for the remote EC2 instances to retrieve objects from the bucket.
- Here is an example policy:
Heads Up!
Be sure to replace
<< content >>with your AWS Account ID's and ARN's.{ "Version": "2012-10-17", "Statement": [ { "Effect": "Allow", "Principal": { "AWS": "arn:aws:iam::<<remote EC2 nodes AWS account ID>>:role/<<ARN associated with remote EC2s>>" }, "Action": [ "s3:GetObject", "s3:ListBucket" ], "Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::automated-diagnostics/*" }, { "Effect": "Allow", "Principal": { "AWS": "arn:aws:iam::<<Process Automation AWS account ID>>:role/<<ARN associated with Process Automation>>" }, "Action": [ "s3:PutObject" ], "Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::automated-diagnostics/*" } ] }
Tip!
You can test that the S3 permissions have been set up correctly by executing a simple script on the remote EC2s through the Systems Manager interface. Follow the instructions outlined in this AWS documentation to set up and run the test.
Setup Within Process Automation
AWS Authentication
Follow the instructions outlined in the AWS Plugins Overview for Process Automation to authenticate with AWS.
Node Discovery
In order to target the remote EC2 instances, they need to be populated into Process Automation's node inventory. It is recommended to use the EC2 Node Source.
When not using the EC2 Node Source
If the EC2 Node Source is not used for node discovery, then be sure that the following node-attributes are added to the nodes:
instanceId- This is the EC2 instance-id from AWS.region- This is the AWS region where the EC2 resides.
Node Attributes can be added when defining a resource-model source manually or by using the Attribute Match node enhancer.
Enable SSM Node Executor
Project Wide Setting
The SSM Node Executor can be set as the Default Node Executor - thereby making it the standard node executor for the whole project:
- Navigate to Project Settings -> Edit Configuration -> Default Node Executor.
- Select the dropdown on the left and select AWS / SSM / Node Executor:
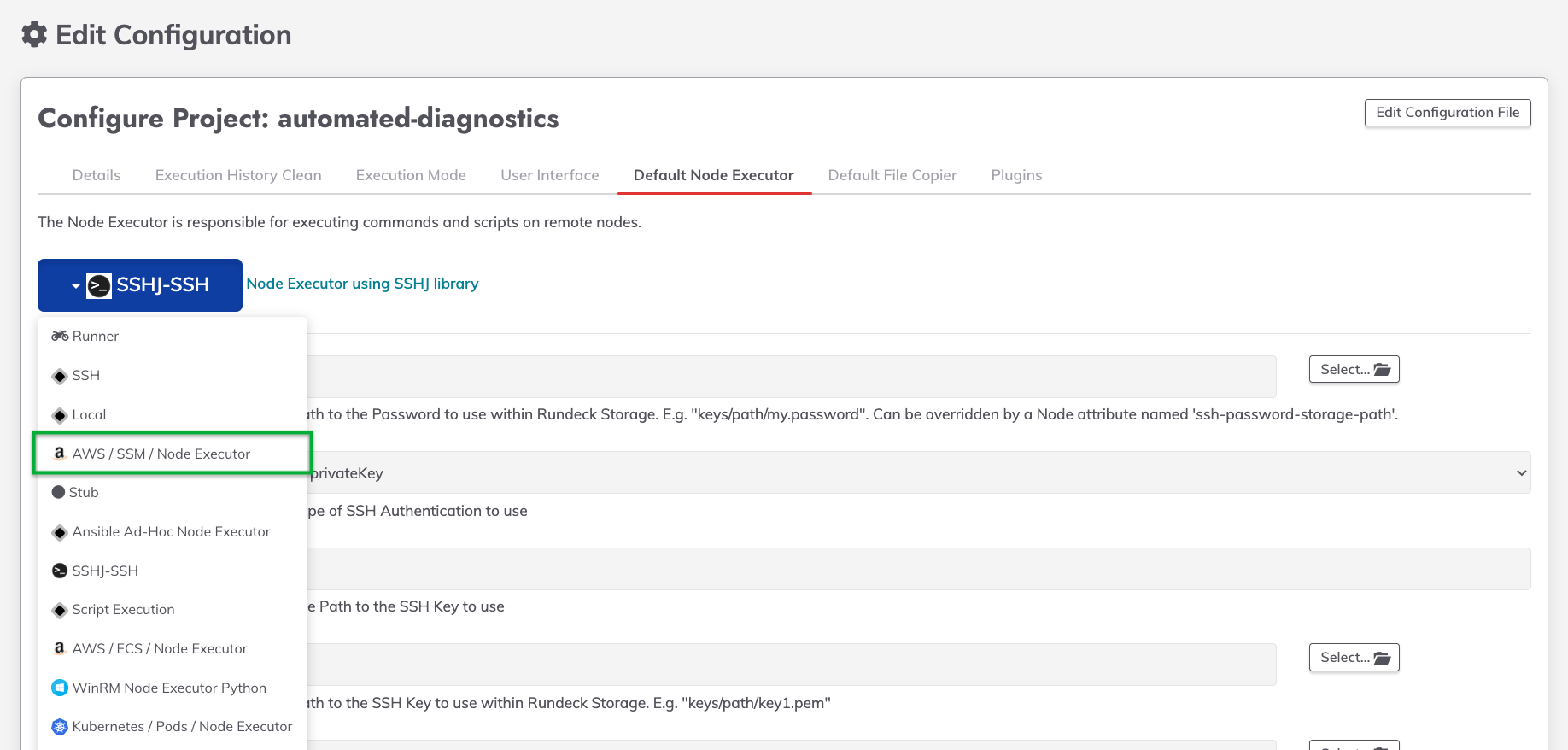
- If Process Automation is authenticated with AWS through an associated IAM Role, then all the fields can be left as their defaults. Otherwise, fill in the Access Key ID and Secret Key fields.
- See below for using CloudWatch Logs for larger log-output.
- Optionally modify the Log Filter Delay property to be the number of seconds to wait before retrieving logs.
Individual Nodes and Node Sources Setting
The SSM Node Executor can alternatively be configured on a per Node Source or per node basis.
To do so, add node-executor=awsssmexecutor as a node-attribute to the nodes.
- For the EC2 Node Source, this can be done using the Mapping Params field:
node-executor.default=awsssmexecutorandfile-copier.default=aws-ssm-copier
Enable SSM File Copier
The SSM File Copier is used to execute scripts and transfer files to EC2 instances. Similar to the SSM Node Executor, it can be configured for an entire project or on per Node Source basis.
Project Wide Setting
The SSM File Copier can be set as the Default File Copier - thereby making it the standard File Copier for the whole project:
- Navigate to Project Settings -> Edit Configuration -> Default File Copier.
- Select the dropdown on the left and select AWS / SSM / File Copier.
- Place the name of the S3 bucket into the Bucket Name field.
- If Process Automation is authenticated with AWS through an associated IAM Role, then the credential fields can be left blank. Otherwise, fill in the Access Key ID and Secret Key fields.
Individual Nodes and Node Sources Setting
The SSM File Copier can alternatively be configured on a per Node Source or per node basis. To do so, add file-copier=aws-ssm-copier and ssm-copier-bucket=S3 bucket name as a node-attribute to the nodes.
Using SSM for Commands and Scripts
Once the setup is complete, commands that are executed on the specified EC2s - either through the Commands tab or through the Remote Command step - will automatically execute through SSM. Similarly, scripts that are executed using the Incline Script Job step will take place using SSM with S3 as the pass-through mechanism.
Using CloudWatch Logs (Optional)
The example policies in the prior sections enable Process Automation to retrieve logs directly from SSM.
However, these logs are truncated to 48,000 characters. To view logs that are longer than this limit, CloudWatch logs are used.
SSM Agent Permissions for Cloudwatch
In order for the log output to be sent to CloudWatch, the SSM agents on the remote EC2 instances need permissions to communicate with CloudWatch.
Add the following IAM permissions to the IAM Role that is associated with the remote EC2 instances:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "logs:DescribeLogGroups",
"Resource": "*"
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"logs:CreateLogGroup",
"logs:CreateLogStream",
"logs:DescribeLogStreams",
"logs:PutLogEvents"
],
"Resource": "*"
}
]
}
Next, add the following permissions to the IAM Role that is associated with Process Automation: logs.GetLogEvents.
Enable CloudWatch Configuring in Process Automation
To use Cloudwatch logs for all SSM output across all nodes that use SSM within the project, specify the CloudWatch Log Group in the Node Executor. Alternatively, add the following to the Mapping Params cloudwatch-log-group.default=<<CloudWatch Log Group Name>> on the node source or with cloudwatch-log-group=<<CloudWatch Log Group Name>> as a node-attribute.
See it in Action
This plugin is used in one of the prebuilt Jobs in our Automated Diagnostics Solution. Try out the Solution to see how this plugin can be used as part of incident-response workflows.
