Process Automation
Process Automation
Process Automation is a server application hosted in a local or private cloud environment as a central administrative control point. Internally, Process Automation stores job definitions and execution history in a relational database. Output from command and job executions is saved on disk but can be forwarded to remote stores like S3 or Logstash.
Process Automation distributed command execution is performed using a pluggable node execution layer that defaults to SSH but plugins allows the use of other means like AWS SSM, Salt, WinRM, or your custom method. Process Automation server configuration includes settings to define the outbound user allowed by the remote hosts. Remote machines are not required to make connections back to the server.
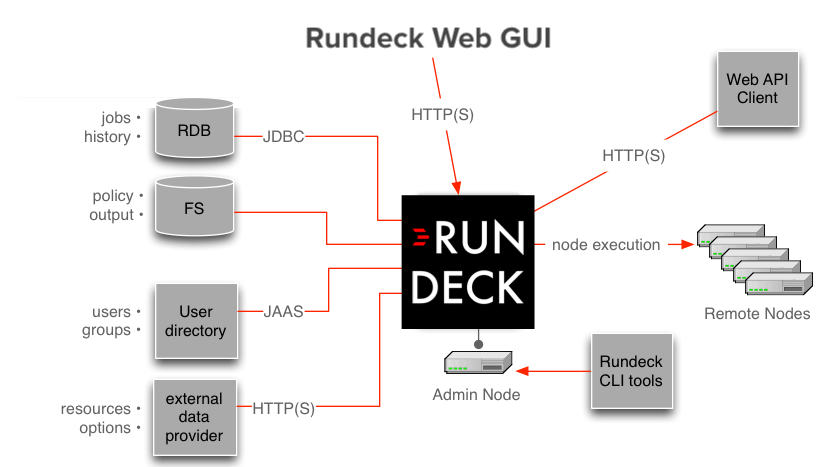
The Process Automation application itself is a Java-based webapp. The application provides both graphical interface and network interfaces used by the Process Automation shell tools.
Access to the Process Automation application requires a login and password. The default Process Automation installation uses a flat file user directory containing a set of default logins and the database for additional users through the User Wizard. Logins are defined in terms of a username and password as well as one or more user groups. An alternative configuration to the flat file user directory, is LDAP (e.g., ActiveDirectory) but Process Automation authentication and authorization is customizable via JAAS. Users must also be authorized to perform actions like define a job or execute one. This is controlled by an access control facility that reads policy files defined by the Process Automation administrator. Privilege is granted if a user's group membership meets the requirements of the policy.
Two installation methods are supported:
System package: RPM and Debian packaging is intended for managed installation and provides robust tools that integrate with the local environment, man pages, shell tools, init.d startup and shutdown.
Launcher: The launcher is intended for quick setup, to get the software running right away. Perfect for bootstrapping a project or trying a new feature.
Process Automation can also install as a WAR file into an external container like Tomcat.
See the Installation section for more details on Process Automation setup.
Assuming the system requirements are met, Process Automation can be installed either from source, system package or via the launcher.
